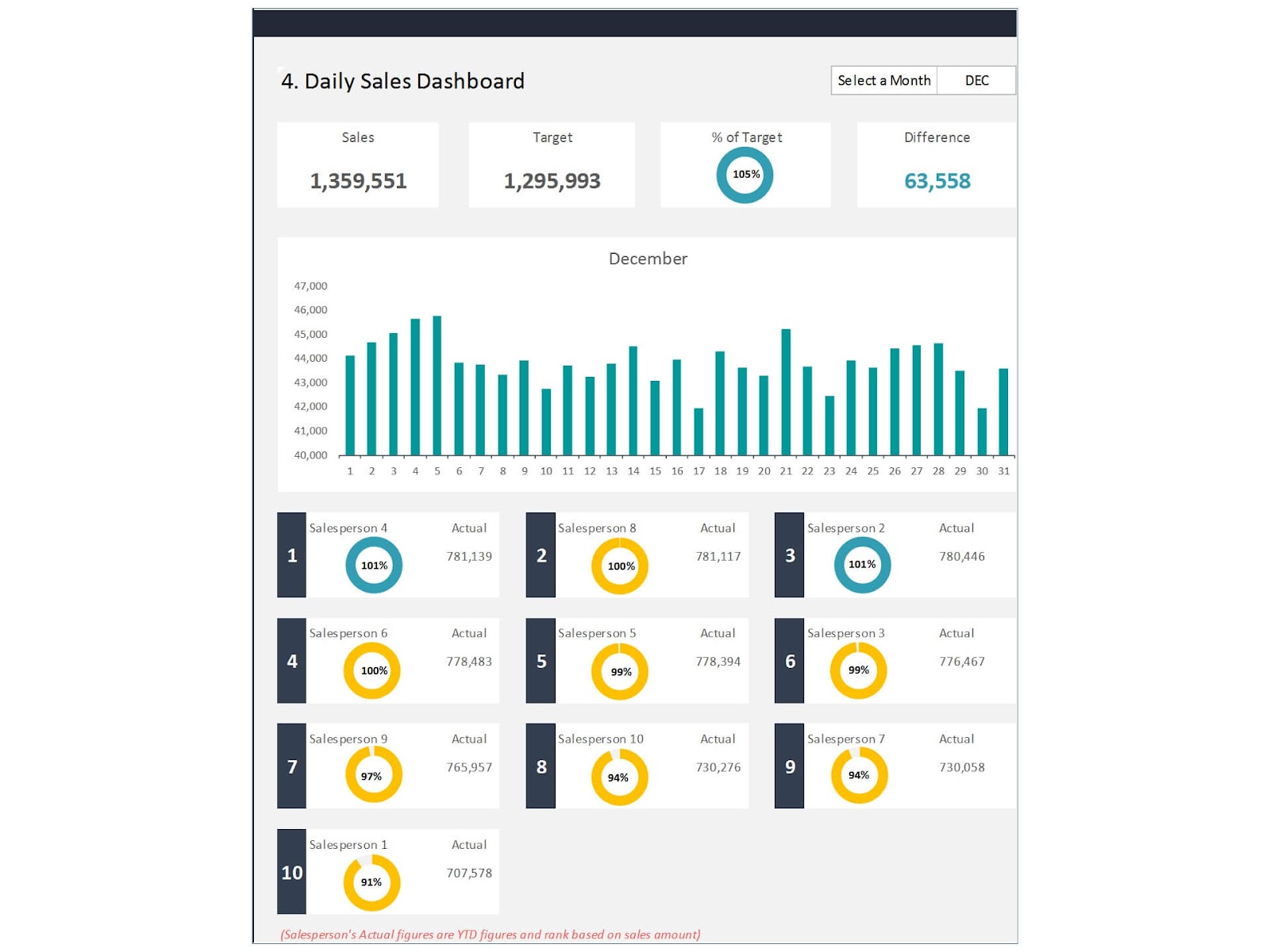
Introduction
A sales tracking dashboard is a useful application that visually describes various data. Its main function is to monitor, evaluate, and report on key details of the sales process. It can also connect with CRM and financial systems for deep analysis of various parameters. Learn the top five essential elements to include in your sales tracking dashboard template to boost efficiency and drive performance.
Using an effective, easy-to-understand dashboard related to sales performance, you can control your team members, monitor the main revenue streams, and spot new sales leads at a glance. This dashboard helps you break down the multiple data fields and offers hints that can turn into calls vital for improving performance levels and, therefore, overhauling operations.
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Selection of relevant KPIs
KPIs refer to measurable values used to assess your company’s performance about a set objective. However, ensure your KPIs match the specific objectives and the set sales targets for the most accurate tracking. A goal such as ‘sell as much as you can’ presents a problem to a company as it is quite possible to miss a measure on whether the team or at least the rep is on track.
Similarly, a sales manager who only focuses on tracking “deals closed” won’t understand areas of underperformance unless “proposals sent” and “demos held” are tracked.
Every company sets different goals. What works for one firm may be the same, such as developing its territories, while the other’s goal is to penetrate deeper into the local market.
Sales goals often fall into two categories:
- Activity goals are measures that involve your team’s direct activity, such as raising the number of first calls for a certain buyer persona.
- Performance-based goals. Targets derived from outcomes, such as enhancing the annual revenues by 25%.
Once you have selected the sales goals, refine them and eradicate the chances of guessing by including the five letters SMART, which stands for specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
Examples of essential sales KPIs
Common examples of sales KPIs include:
- Sales revenue
- Number of new customers
- Sales conversion rate
- Average sale value
- Sales growth rate
- Quantity of sales by quantity of salespeople
- Sales cycle length
- Lead-to-customer conversion rate
- Sales forecast accuracy
Here are four of the most important sales KPIs to keep an eye on:
Sales Revenue:
It is crucial to note that the percentage of meetings held is regarded as the most elemental and important KPI of any sales team. Cost Of Sales’ means the total receipt of money on goods sold, commonly called gross sales. The metric will enable a business to determine the expected revenues and make inaccurate estimations of future revenues.
Close rate:
This metric determines an organization’s ability to drive the leads to become its customers. The high close rate proves salespeople are good at following up on potential customers and clinching the cheques. On the other hand, a low close rate may result from defective last steps of the selling routine or inappropriately filtered leads.
Calculate it: ((Number of Conversions / Number of Total Leads) x 100).
Average deal size:
This relates to the ratio of total revenues to the number of sales and determines the average revenue per sale. Large Average Deal sizes suggest that the organization’s product or service sales are of higher value and that the sales team targets higher-value deals. Small Average Deal sizes indicate that the organization is targeting smaller-value deals.
How to calculate it: The won-closed ratio is calculated as the total value of all the closed won opportunities divided by the total number of opportunities.
Lead conversion rate:
This metric defines the turnover ratio of leads to opportunities. It also shows that your sales team can qualify leads based on the information you provided; otherwise, your leads are being wasted.
Customer lifetime value (CLV)
What it measures: Total amount of all the subsequent transactions that a customer makes with your company during their lifetime.
CLV serves practical and instructive purposes when showing your team’s capability of creating the needed trustworthy, value-oriented, and loyal customer base, which brings upsell, cross-sell, renewals, and predictable revenue. So, if the CLV is low, one needs to revisit the call transcripts of the most valuable customers.
How to calculate: Purchased per customer per year x the frequency of customer’s visits x average length of customer’s lifetime = CLV
Visualization tools
Choosing the right charts and graphs
The sales dashboard’s choice of charts and graphs is essential for increasing its effectiveness. Some of the trends that are easily followed on line charts include the position of a business over a specific period, while bar charts are handy when analyzing a business based on different categories. Pie charts help demonstrate proportions, while scattergrams can aid in finding relations. Heat maps are also good when emphasizing data by geographic or hierarchical structure. Select the most appropriate type of visualization to improve learning and discovery.
Real-time data visualization
Data refreshes in dashboards have some advantages. They provide fresh analysis, hence facilitating quick decision-making. This little feature increases orientation to changing conditions, bringing more strategic and unintentional planning flexibility. Real-time visualization also makes the process and information transparent by providing the most updated data to the stakeholders, which helps to make better and more accurate decisions.
Customizable filters
Importance of flexibility in data analysis
Filters in a sales tracking dashboard must be flexible since every team can have different requirements. They allow setting conditions to use data and thereby sorting data based on certain conditions to get a unique interpretation of it. This flexibility augments user involvement and satisfaction since the teams have a chance to customize the dashboard to satisfy their needs, hence improving decision-making and performance.
Examples of effective filters
Filters based on periods, the regions of sales, and the categories of products will improve the data analysis in a sales tracking dashboard. Some options under time filters could be daily, weekly, monthly, or setting your range. Filters functioning as sales regions could have country, state, and territory selections. In terms of the product dimension, other options could let users narrow their search to specific genera or types of products to obtain results for a specific genre or product type that would be used for targeted analysis and specific actions regarding the findings on each dimension.
Integration capabilities
Syncing with existing sales tools
There must be synchronization with CRM and other sales tools used in the organization to avoid Data Duplication and repetition of work. Integrating with the existing tools, the dashboard holds all the information displayed about sales performance, communications, and pipeline. This integration optimizes workflows, reduces input error, and makes sure that various teams in an organization receive up-to-date information that can help in decision-making and adjustment of strategies.
Automation of data inputs
The use of integration and automation in a sales tracking dashboard template is useful in entering that database inputs in the dashboard which saves time and eliminates possible errors brought about by manually entering data. This guarantees that information from sources like Customer Relationship Management systems or spreadsheets is captured and updated in real-time. It reduces or eliminates the need for assembly-line work and manual data entries, thus reducing decision-making errors and improving data quality.
Actionable insights
Translating data into strategy
When designing for insights, data is communicated in dashboards, which are brief and specific and usually come with elaboration. Employ charts and graphs that display some values and tendencies in their focus and add comments or descriptions as a tooltip. The business intelligence solution must include drill-downs and filters for further analysis. Include a disclaimer stating that the results are not intended to be used as the final output but as a recommendation or the next step to facilitate a strategic management decision.
Alert and notification features
Having alert and notification options in a sales tracking dashboard helps the team constantly monitor for any changes in status by constantly updating the dashboard about essential changes in figures or events. Conduct KPI monitoring and define critical acceptable values that cause alert generation, like the amount of sales and changes in the pipeline amount. This makes it possible to respond to new events quickly, either deal with adverse events or take advantage of positive ones.
Conclusion
A well-designed sales tracking dashboard incorporates five essential elements: The various features include the following: sales revenue, close rate, average deal size, conversion rate, and customer lifetime value, among others. In turn, such a dashboard helps simplify the data analysis process, giving instant access to such values, which is critical for the specific decision that has to be made. Having a small business coach is beneficial for identifying and refining your business KPIs to ensure they align with your overall business objectives and growth strategies.-
As a consequence, coordinating tasks improves sales productivity, while the status of the pipeline and customer interactions increase its efficacy. As it is presented, Biz Infograph team is able to identify trends, opportunities, or challenges on a real-time basis with its amaizng dashboards. They can modify their sales strategies and increase their productivity, sales, and value delivery to their clients.