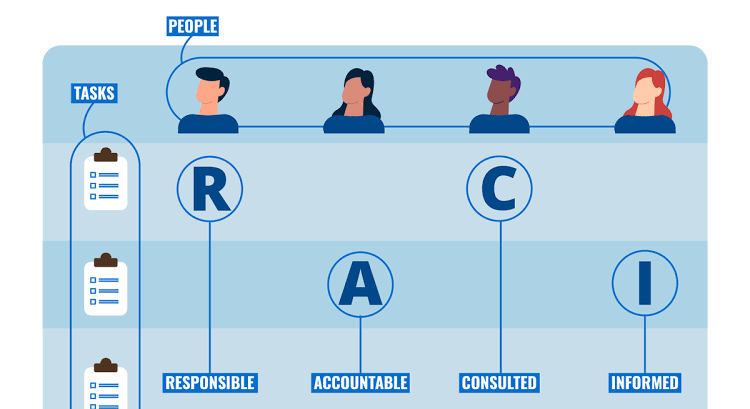
The RACI matrix, also known as the RACI chart or RACI model, is a popular project management tool designed to clarify roles and responsibilities within a project, ensuring effective collaboration among all stakeholders. RACI charts are project management tools that clarify roles and responsibilities.
The acronym RACI stands for Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed, each representing a distinct role in the project’s workflow. RACI charts and the RACI matrix are essential tools for defining and clarifying roles and responsibilities in project management.
Origins of the RACI Matrix
The exact origins of the RACI matrix are hard to pinpoint. It has evolved over time and has been adopted by various organizations. Notably, Edmond F. Sheehan and the DuPont Corporation have been credited with its development, along with Ernst & Young, which utilized a similar model called the RASCI matrix. The RASCI adds an additional role, Supportive, to further clarify task responsibilities.
Components of the RACI Matrix
Responsible (R): The individual(s) who complete the task. They are the hands-on people doing the work.
Accountable (A): The person who owns the task. They ensure it is completed correctly and on time, often delegating the work to those responsible.
Consulted (C): Those whose opinions are sought. They provide valuable input but do not carry out the task themselves.
Informed (I): Individuals who need to be kept updated on progress and decisions but do not directly contribute to the task.
Applications of the RACI Matrix
The RACI matrix is particularly useful for large, complex projects involving multiple stakeholders and cross-departmental collaboration. It helps eliminate confusion by clearly defining roles and responsibilities, ensuring that everyone knows their part in the project.
Examples of When to Use a RACI Matrix
Large-scale projects: Company-wide DEIB training involving all departments and multiple stakeholders.
Projects with lengthy decision-making processes: Implementing new performance management systems.
Situations with potential conflicts about task ownership: Revising the company’s code of conduct.
Projects with multiple departments: Ensuring clear communication and role definition across teams.
High turnover rates: Quick onboarding of new members to specific roles.
When Not to Use a RACI Matrix
Small projects: Teams that communicate well and manage their tasks efficiently.
Agile frameworks: Roles and responsibilities are already clearly defined in methodologies like Scrum.
Benefits of the RACI Matrix
Clarity: Clearly defines who is responsible for each task, reducing confusion.
Accountability: Assigns ownership of tasks, making it easier to hold people accountable.
Improved Communication: Facilitates communication by identifying who needs to be consulted and informed.
Better Decision-Making: Ensures the right people are involved in decisions.
Increased Efficiency: Streamlines processes by eliminating unnecessary steps.
Better Coordination: Helps coordinate work among different teams, reducing delays and missed deadlines.
Drawbacks of the RACI Matrix
Time-Consuming: Creating a RACI chart can be labor-intensive, especially for complex projects.
Inflexibility: Once established, making changes to the matrix can be challenging.
Overly Restrictive: May prevent team members from taking on additional responsibilities.
Lack of Buy-In: Team members may resist roles assigned without their input.
Limited Scope: May not account for the entire scope of a project.
Complexity: Large projects can complicate the matrix, leading to oversimplification.
Creating a RACI Matrix: Steps
List Project Tasks: Identify all tasks, milestones, and decisions required for the project.
Identify Roles: List all team members and stakeholders involved.
Assign RACI Roles: Assign Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed roles to each task.
Share the Matrix: Ensure all team members understand their roles and responsibilities.
Best Practices
- Assign only one responsible and one accountable person per task.
- Continually update and revise the matrix to reflect project changes.
- Avoid overcomplicating the matrix with unnecessary details.
Alternatives to the RACI Matrix
RASCI: Adds a Supportive role to indicate those who assist in completing tasks.
CARS: Focuses on communication, approval, responsibility, and support.
DACI: Uses Drivers, Approvers, Contributors, and Informed to clarify actions.
CLAM: Focuses on contributions, leadership, approval, and monitoring.
Using a RACI Matrix in Practice
Identify Project Roles Create a table listing out the names or roles of everyone involved in the project at the top. Traditionally, RACI charts list the functional roles along the top. However, using names can sometimes be more effective, especially for smaller teams.
Identify Project Tasks or Deliverables Break the project down into clear tasks and deliverables. This step involves listing these tasks in the left-hand column of your chart. Try not to go too granular; aim for a balance that avoids overwhelming detail but provides enough specificity to be useful.
Assign the RACI Roles to Each Task Work through each task and decide what each role should be responsible for. Every task should have someone responsible and accountable. Think about who should be consulted during the task and who should be informed once it’s complete.
Agree on the RACI Matrix with Your Team Align on any assumptions with your team members, and do not create the matrix in isolation. Have a discussion to ensure everyone is happy with their roles and responsibilities on the project.
Get Approval from Core Project Stakeholders Set up a meeting to agree on the matrix with key stakeholders. Keep this as lean as possible to avoid lengthy discussions. Ensure that those who need to be communicated with are kept in the loop.
Make the RACI Matrix Useful Throughout the Project Refer back to the RACI matrix during the project to ensure roles and responsibilities remain accurate. Host it online using project management software for easy access. At the project’s end, review how well the RACI assignments worked and make adjustments for future projects.
Practical Examples of RACI Matrix Usage
Implementing a New Performance Management System In this scenario, the HR team needs to define who will determine the system’s core objectives, choose the software, and train employees. A RACI matrix can clarify who is responsible for each task, who needs to approve decisions, who provides input, and who needs to be kept informed of progress.
Planning a Company-Wide DEIB Training For a large-scale diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging (DEIB) initiative, the RACI matrix ensures clear communication across all departments. It designates who will create the training materials, who will deliver the sessions, and who will monitor attendance and feedback.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of RACI Matrix
Pros:
Clear Expectations: Sets clear expectations for task management and responsibility.
Streamlined Communication: Helps avoid involving everyone in every decision, speeding up sign-offs.
Reduced Overload: Prevents overloading individuals with responsibilities and reduces siloing.
Cons:
Time-Consuming Creation: Building the matrix can take significant time and effort.
Risk of Inflexibility: The matrix may become outdated if project roles change frequently.
Potential for Over-Restriction: Might limit team members from taking on additional tasks.
Alternatives to the RACI Matrix
RASCI: Adds a Supportive role to indicate those who assist in completing tasks. CARS: Communicate, Approve, Responsible, Support – focuses on task-specific actions. DACI: Drivers, Approvers, Contributors, Informed – action-oriented terms. CLAM: Contributes, Leads, Approves, Monitors – focuses on task contributions and monitoring.
Overall, the RACI matrix remains a vital tool in project management, ensuring that all stakeholders are aligned and that projects are executed efficiently and effectively. By understanding its components, applications, and potential drawbacks, organizations can leverage the RACI matrix to enhance their project outcomes.
Stay in touch to get more news & updates on Gossips.blog!