Vestibular physiotherapy for ataxia focuses on addressing issues related to balance and coordination caused by dysfunction in the vestibular system, encompassing the inner ear and its connections to the brain. Vestibular physiotherapy in Grande Prairie aims to optimize the functioning of the vestibular system, improve balance and coordination, and enhance the individual’s ability to perform daily activities safely and independently despite the challenges posed by ataxia.
What is Vestibular Ataxia?
Vestibular ataxia is a neurological condition stemming from dysfunction within the vestibular system, which regulates balance and spatial orientation. This impairment can lead to symptoms such as dizziness, vertigo, unsteadiness, and difficulties with walking or maintaining balance. Individuals with vestibular ataxia may experience a sensation of spinning (vertigo) or feel as though they are swaying or floating. They may also have trouble coordinating movements, particularly when walking or navigating their environment. These symptoms can have a considerable effect on an individual’s quality of life, causing limitations in daily activities and increasing the likelihood of experiencing falls.
Physiotherapy Methods Used To Improve Gait Stability:
Vestibular physiotherapy in Grande Prairie plays a crucial role in managing ataxia and enhancing gait stability. Here are some common approaches used by physiotherapists:
Balance and proprioceptive training:
These exercises focus on improving the patient’s ability to maintain balance and spatial orientation. This may involve standing on unstable surfaces, such as foam pads or balance boards, and performing various movements to challenge balance control. Here are some specific exercises commonly used:
Single-leg stance:
Balancing on a single leg while maintaining stability is a fundamental proprioceptive exercise. Patients can start by holding onto a stable surface for support and gradually progress to standing unsupported.
Dynamic balance exercises:
These exercises entail executing dynamic movements while sustaining balance, including walking in various directions, shifting weight from side to side, or rotating the trunk while standing on an unstable surface.
Gaze stabilization:
Vestibular ataxia often leads to impaired gaze stability, which can affect walking ability. Gaze stabilization exercises and techniques involve moving the head and eyes while focusing on a stationary object to improve the coordination between the vestibular system and eye movements.
Smooth pursuit exercises:
Patients track a moving target with their eyes while keeping their heads still. This helps improve the smoothness and accuracy of eye movements, enhancing visual tracking ability during head movements.
Optokinetic stimulation:
Patients watch a moving visual pattern, such as stripes or dots on a rotating drum or computer screen, while keeping their heads still. This stimulates the vestibular-ocular reflex and helps improve the coordination between head movements and eye movements.
Gait training:
Physiotherapists work on improving the patient’s walking pattern by addressing issues such as instability, uneven step length, and poor coordination. This may involve practicing walking on different surfaces, utilizing assistive devices like canes or walkers if necessary, and focusing on proper foot placement and weight shifting.
Assistive device training:
Patients learn how to use assistive devices such as canes, walkers, or walking poles to improve stability and reduce the risk of falls. Physiotherapists provide instruction on proper device use and gait mechanics to optimize walking safety and efficiency.
Cued walking:
Patients practice walking with verbal or visual cues to improve gait symmetry, step length, and timing. Cues may include metronome beats, visual markers on the ground, or verbal instructions to encourage specific walking patterns.
Dual-task training:
Patients perform cognitive tasks simultaneously with walking, such as counting backward or reciting a sequence of numbers. This challenges attentional resources and helps improve the ability to maintain gait stability while multitasking.
Strength and flexibility exercises:
Enhancing the strength of muscles surrounding the ankles, knees, and hips may improve stability and reduce the risk of falls. Flexibility exercises aid in preserving the range of motion in the joints, which is important for smooth and coordinated movement during walking. Here are some common strength and flexibility exercises used in physiotherapy:
Ankle strengthening exercises:
- Calf raises: Patients stand with their feet hip-width apart, rise onto the balls of their feet, and then lower back down.
- Ankle dorsiflexion/plantarflexion exercises: Patients move their ankles up and down against resistance, using resistance bands or manual resistance from a therapist.
Knee strengthening exercises:
- Quadriceps strengthening: Patients perform leg extensions while sitting or lying down, lifting the lower leg against resistance.
- Hamstring curls: Patients flex their knees against resistance, either with a resistance band or using weight machines.
Hip strengthening exercises:
- Hip abduction/adduction exercises: Patients perform leg lifts to the side and across the body against resistance to strengthen the muscles that stabilize the hips.
- Hip extension exercises: Patients perform exercises to extend the hip joint, such as hip bridges or prone leg lifts.
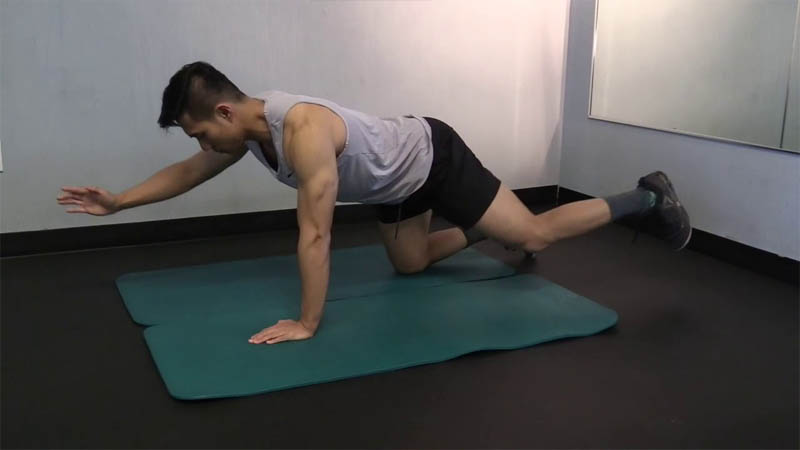
Core strengthening exercises:
- Planks: Patients hold a plank position, either on elbows or hands, to strengthen the core muscles.
- Bridge exercises: Patients lie on their back with their knees bent and lift the hips off the ground to engage the core and glute muscles.
Flexibility exercises:
- Calf stretches: Patients perform calf stretches against a wall or utilizing a towel to stretch the calf muscles.
- Quadriceps stretches: Patients pull one foot toward the buttocks while standing or lying down to stretch the quadriceps muscles.
Enhancing Gait Stability and Independence:
Vestibular physiotherapy in Grande Prairie plays a vital role in enhancing gait stability for individuals with vestibular ataxia. By targeting specific deficits within the vestibular system and integrating sensory inputs from other systems, such as vision and proprioception, GP Pain Physiotherapy in Grande Prairie employs vestibular rehabilitation techniques to help individuals with vestibular ataxia improve their ability to maintain balance and navigate their environment safely. By empowering patients with strategies to manage symptoms and minimize the risk of falls, vestibular rehabilitation therapy empowers individuals to engage more fully in daily activities and maintain independence in their daily lives.
Stay in touch to get more updates & news on Gossips!